Configuring Your Audio and MIDI
Jack Connections
Jack is an audio and midi connections tool. We will be using it to create and test connections between MIDI hardware devices and Virtual MIDI devices, and between Audio Channels and Audio Effects.
Jack Settings
-
Right click on the Jack Control icon on the bottom left side of the task bar
-
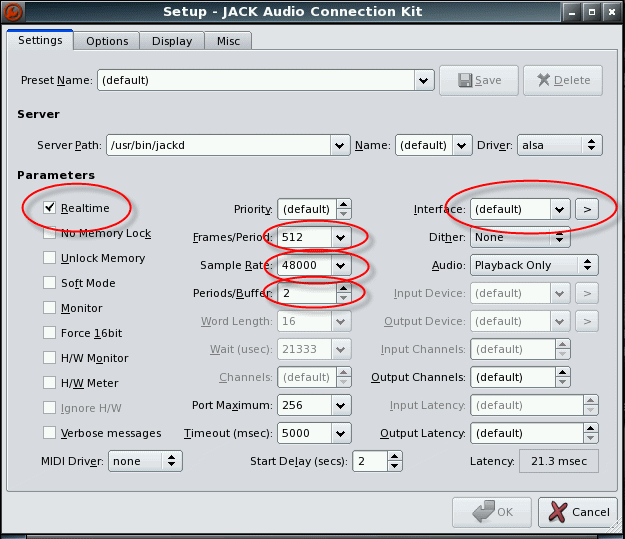
Select 'Setup' from the Jack Control menu that appears
-
The settings shown here are a good starting point for most computers/soundcards
-
Click on the '>' button of the 'Interface' option to see the list of audio devices on your system
-
If you have more than one soundcard, select the one that jOrgan will be using from this list
-
If you are using an older computer or a slower CPU, deselect the 'realtime' option
-
A lower Frames/Period will equal lower latency, so experiment with this value
-
Higher Frames/Period and Periods/Buffer values increases latency but also increases stability of the audio stream. So if you experience crackles, pops, or other bang type noises experiment with higher values (distortion can also be caused by amplitude values being too high for your audio system, so if you are experiencing distortion also check the fludisynth gain values in the jOrgan Customize wizard of the disposition that you are playing)
Creating Connections from your Hardware MIDI device to a Virtual MIDI device
In my setup I configure all the jOrgan dispositions to use the first Virtual MIDI device for the keyboard elements, and then connect all three of my MIDI devices (my two MIDI Keyboards and a MIDIfied Pedalboard) to that Virtual MIDI device in the ALSA tab of Jack Control. I have also created a patchbay setting that retains these connections each time I boot into jOrgan Pup (more on the patchbay later).
-
Right click on the Jack Control icon on the bottom left side of the task bar
-
Select 'Connections' from the Jack Control menu that appears
-
The Connection screen will now show, and you will see three tabs indicating the three types of connections available - Audio, MIDI, and ALSA.
-
Note: ALSA stands for Advanced Linux Sound Architecture and that tab will contain all the installed hardware MIDI devices and the configured Virtual MIDI devices. The MIDI tab configures Jack MIDI ports which require specific software drivers with the application. Fluidsynth will be using ALSA MIDI ports by default and so these will only appear in the ALSA tab.
-
Click on the ALSA tab. You will see all the MIDI Out devices (those that are sending MIDI data) on the left had side, and all the MIDI In devices (those that are receiving MIDI data) on the right.
-
Click on the (+) node of one of the devices to expand the device node and show the available MIDI Ports
-
To connect a hardware MIDI keyboard to a virtual MID device and Port, click on the name of the MIDI device in the left hand column, then click on the Virtual MIDI device in the right hand column, and then click on the 'Connect' button.
Modifying Connections
You can disconnect Jack connections and make new connects that suit your particular hardware setup.
Next : Working with Convolution Reverb
Navigation